Bitdefender Threat Debrief | April 2022

Highlight of the month:MITRE ATT&CK Evaluations 2022
Security practitioners are familiar with the MITRE ATT&CK Framework, but they are often not familiar with another related project – MITRE ATT&CK Evaluations. This year, 30 security vendors were tested on their ability to detect ransomware and wiper deployments and then provide analytical insights.
The results provided are extensive, but there are no scores, rankings, or ratings. Instead, the evaluations show how each vendor approaches threat detection in the context of the ATT&CK®knowledge base.
Every year, some vendors use misleading practices when interpreting the results of MITRE and other evaluations. The best prevention is to learn how to interpret the results.
Below are some short videos of the most common misleading claims and strategies:
- Claiming to be number #1
- Comparing apples and oranges
- Presenting just part of the data
- Ignoring different needs and requirements
- Using euphemisms and focusing on steps
When evaluating the results, we recommend drawing your own conclusions and not solely relying on interpretations by security vendors (even our own).
Ransomware Report
Spear phishing attacks are often used as an initial attack vector and ransomware infection is often the final stage of the kill chain. For this report, we analyzed malware detections collected in March 2022 from our static anti-malware engines. Note: we only count total cases, not how monetarily significant the impact of infection is. Opportunistic adversaries and some Ransomware-as-a-Service (RaaS) groups represent a higher percentage compared to groups that are more selective about their targets, since they prefer volume over higher value.
When looking at this data, remember these are ransomware detections, not infections.
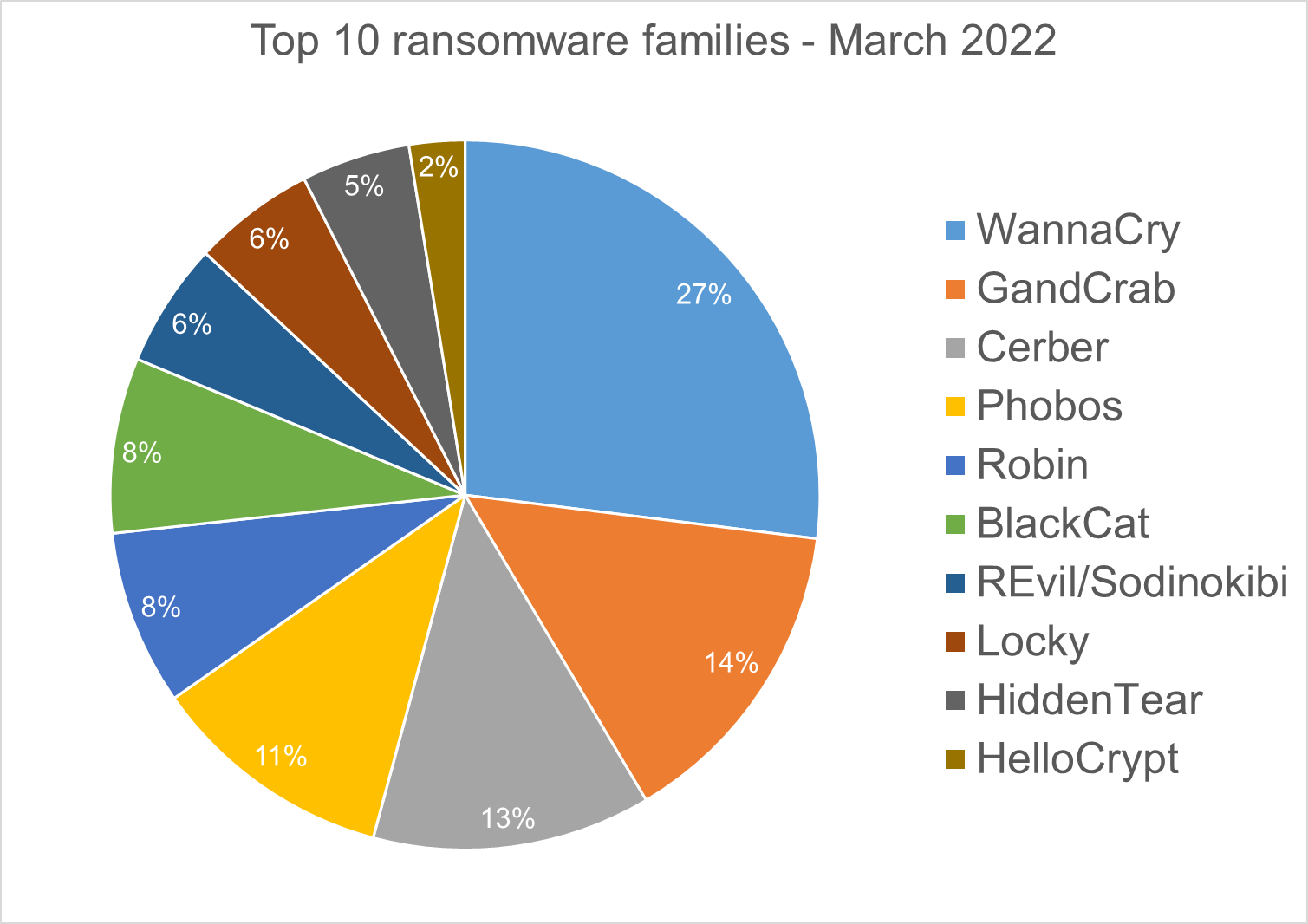
Top 10 Ransomware Families
We analyzed malware detections from March 1 to March 31. In total, we identified 222 ransomware families. The number of detected ransomware families can vary each month, depending on the current ransomware campaigns in different countries.
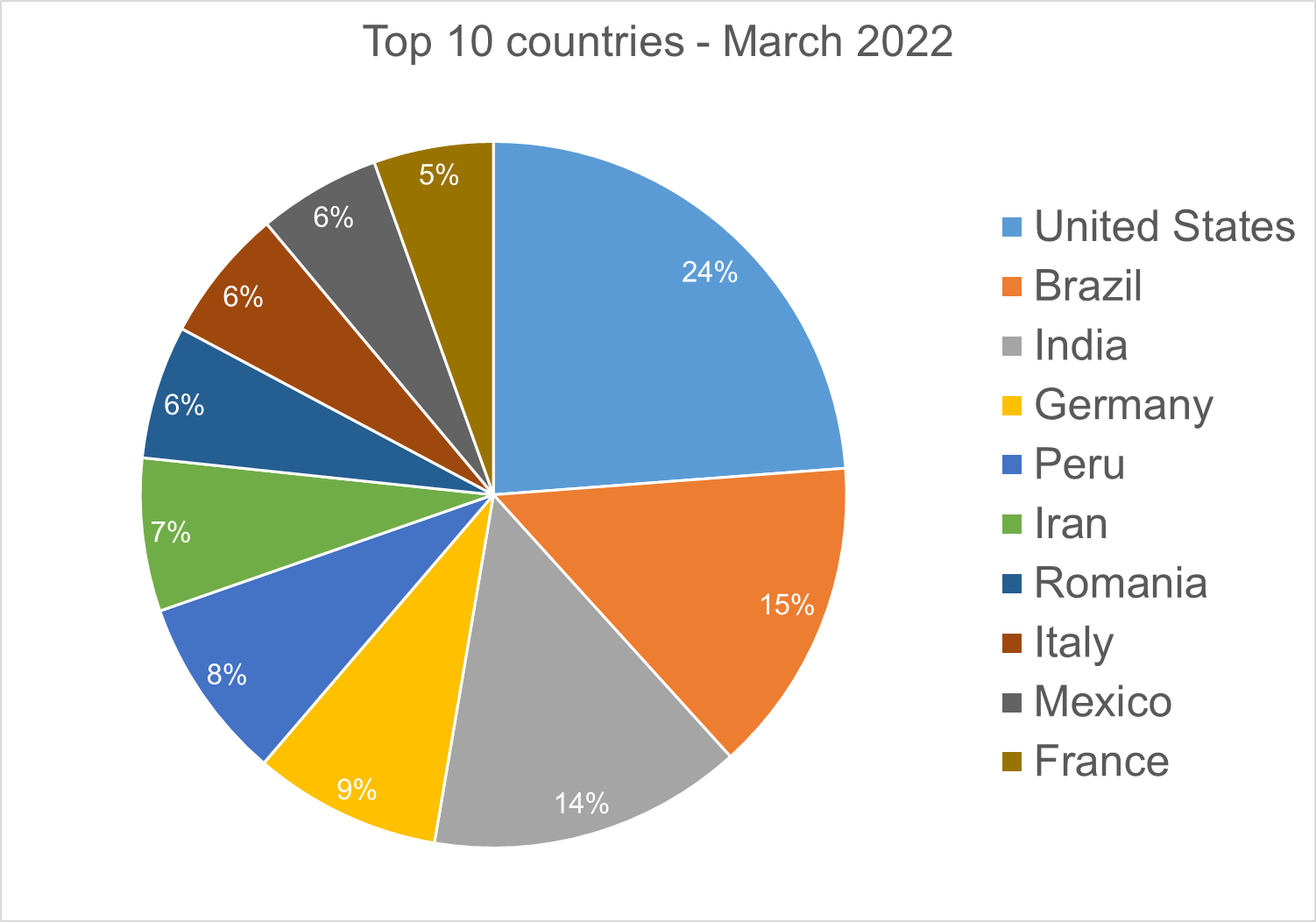
Top 10 Countries
In total, we detected ransomware from 155 countries in our dataset this month. Ransomware continues to be a threat that touches almost the entire world. Below is a list of the top 10 countries most impacted by ransomware. Many ransomware attacks continue to be opportunistic, and the size of population is correlated to the number of detections.
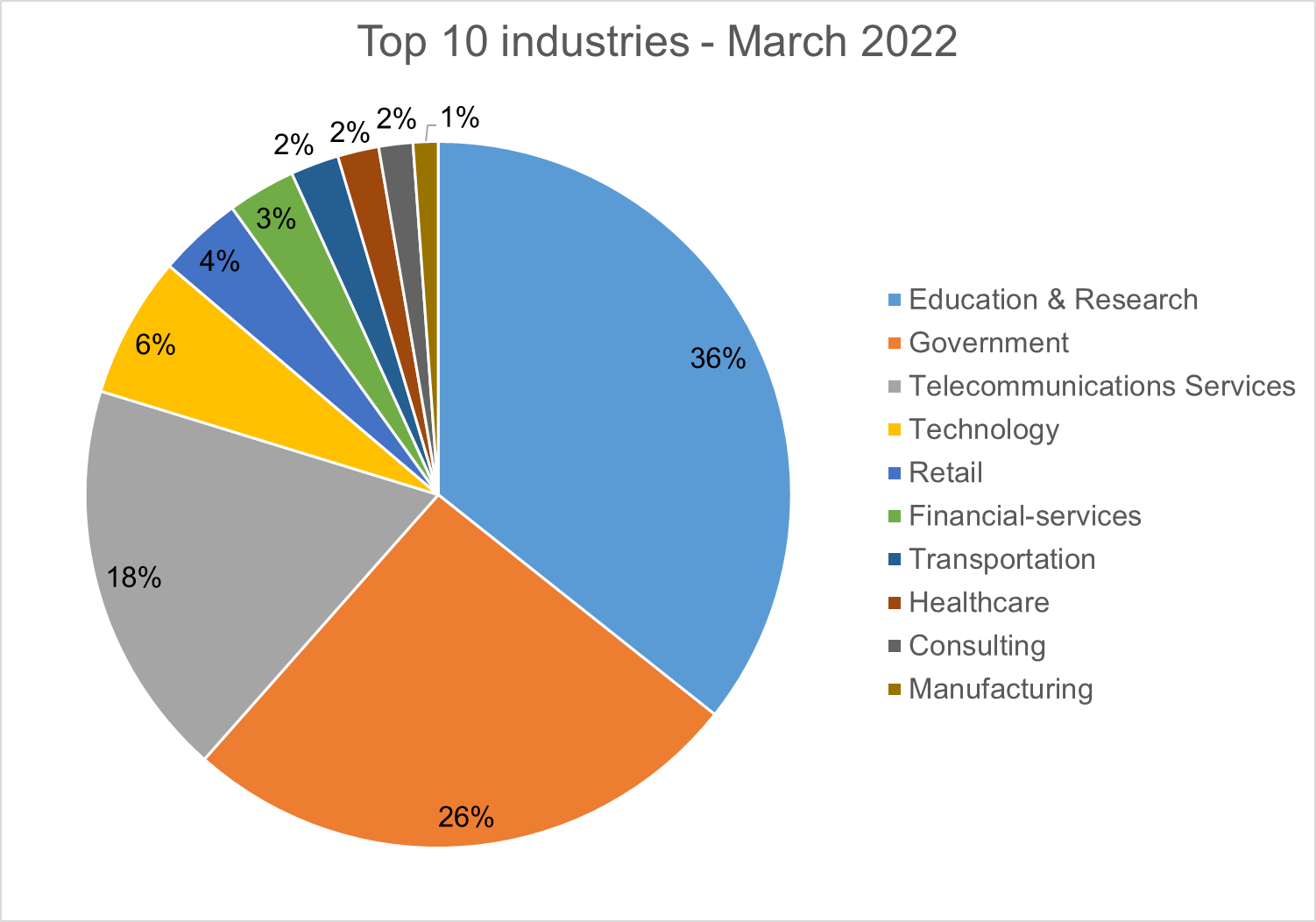
Top 10 Industries
For our dataset, we have been able to assign 21% of detections to specific industries. Telecommunications services are particularly high as their customers are included within the detections.
Android trojans
Below are the top 10 trojans targeting Android we have seen in our telemetry during March 2022.
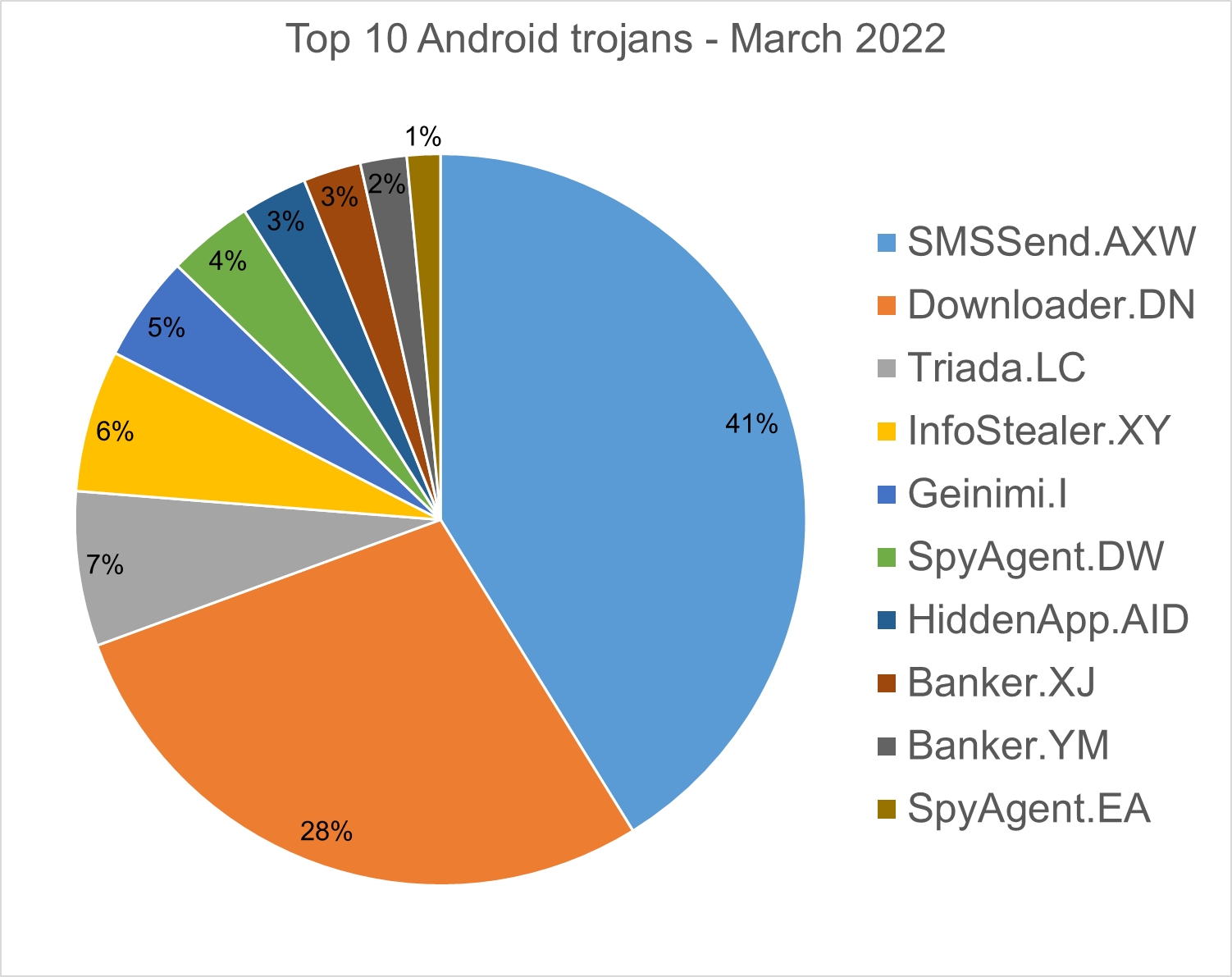
SMSSend.AXW – Malware that tries to register as the default SMS application on the first run by requesting a consent of the user. If successful, it collects the user’s incoming and outgoing messages and forwards them to a Command & Control (C&C) server.
Downloader.DN – Repacked applications taken from Google App Store and bundled with aggressive adware. Some adware downloads other malware variants.
Triada.LC – Malware that gathers sensitive information about a device (Device IDs, Subscriber IDs, MAC addresses) and sends them to a malicious C&C server. The C&C server responds by sending back a link to a payload which the malware downloads and executes.
InfoStealer.XY – Obfuscated applications that masquerade as mobile antiviruses. When the malware app is first run, it checks if there is any AV solution installed and it tricks the user to uninstall it. It exfiltrates sensitive data, downloads and installs other malware, and displays adware.
Geinimi.I – Applications that have been repacked with aggressive adware.
SpyAgent.DW – Applications that exfiltrate sensitive data like SMS messages, call logs, contacts, or GPS location.
HiddenApp.AID – Aggressive adware that impersonates adblock applications. When running for the first time, it asks permission to display on top of other apps. With this permission, the application can hide from the launcher.
Banker.XJ, YM – Applications that drop and install encrypted modules. This trojan grants device admin privileges, and gains access to manage phone calls and text messages. After deploying, it maintains a connection with the C&C server to receive command and upload sensitive information.
SpyAgent.EA– Applications that exfiltrate sensitive data.
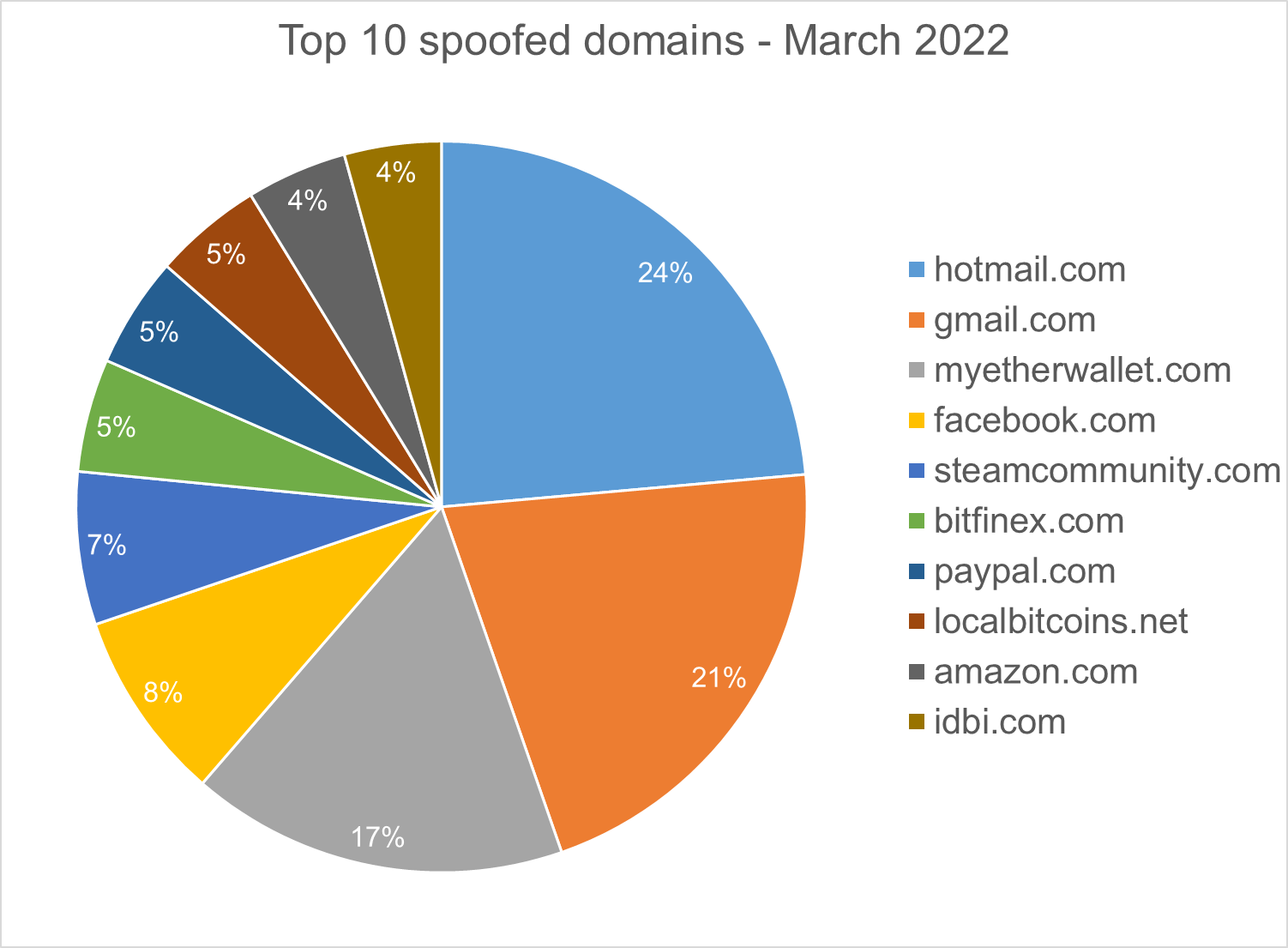
Homograph Phishing Report
Homograph attacks work to abuse international domain names (IDN). Threat actors create international domain names that spoof a target domain name. When we talk about “target” of IDN homograph phishing attacks, we refer to the domain that threat actors are trying to impersonate. You can read more about this type of attack in one of our previous reports.
Below is the list of the top 10 most common targets for phishing sites.
About Bitdefender Threat Debrief
The Bitdefender Threat Debrief (BDTD) is a monthly series analyzing threat news, trends, and research from the previous month. Don’t miss the next BDTD release, subscribe to the Business Insights blog, and follow us on Twitter. You can find all previous debriefs here.
Bitdefender provides cybersecurity solutions and advanced threat protection to hundreds of millions of endpoints worldwide. More than 150 technology brands have licensed and added Bitdefender technology to their product or service offerings. This vast OEM ecosystem complements telemetry data already collected from our business and consumer solutions. To give you some idea of the scale, Bitdefender Labs discover 400+ new threats each minute and validate 30 billion threat queries daily. This gives us one of the industry’s most extensive real-time views of the evolving threat landscape.
Wewould like to thank bitdefenders Alin Damian, Mihai Leonte, Ioan Marculet, Andrei Mogage, Ioan Stan, Marius Tivadar, and Horia Zegheru (sorted alphabetically) for their help with putting this report together.
