
The Bitdefender Threat Debrief (BDTD) is a new monthly series analyzing ransomware news, trends, and research from the previous month.
From our petri digi-dish
In this section, we highlight some of the research from our own Bitdefender Labs:
- FIN8 is an established threat actor that takes extended breaks to improve their tactics, techniques, and procedures. Each new version of their toolkit starts with small tests on a limited pool of victims before launching a full-scale attack. If you want to learn about their latest update, read our blog post Deep dive into a FIN8 attack – A forensic investigation.
- Our security researchers discovered a new group deploying Monero mining malware. Their specialty is weak SSH credentials – and there’s no shortage of Linux targets to compromise. Unfortunately, brute force still works – it’s simple and effective. Learn more about this new group – How We Tracked a Threat Group Running an Active Cryptojacking Campaign.
- The journey of Trickbot started almost half a decade ago when it appeared in the form of a banker and credential-stealing application. Over the years, it evolved into an ecosystem with many modules. There is an updated Virtual Network Computing (VNC) module in active development – read more about it – A Fresh Look at Trickbot’s Ever-Improving VNC Module.
World in numbers
Bitdefender provides cybersecurity solutions and advanced threat protection to hundreds of millions of endpoints worldwide. More than 150 leading technology brands have licensed and added Bitdefender technology to their product or service offerings. This vast OEM ecosystem complements telemetry data already collected from our business and consumer solutions. To give you some idea of the scale, our Labs operations discover 400+ new threats each minute and validate 30 billion threat queries daily. This gives us one of the industry’s most extensive real-time views of the evolving threat landscape.
For this report, we analyzed malware detections collected in July 2021 from our static anti-malware engines. Modern endpoint protection platforms use multiple layers of defense – and static engines are one of the first lines of security, identifying malicious code based on previously known attributes (for example, known malicious file hash or file certificate).
Note: data from machine learning and other advanced modules are not included. These modules are specialized in detecting code that exhibits malicious behavior, but identification of specific ransomware families is complicated. Detections are often based on calculating probability, and attribution is not as binary as with static detections.
When looking at this data, it is crucial to understand that these are ransomware detections, not infections. Detection rates vary based on technologies in place and dedicated resources.
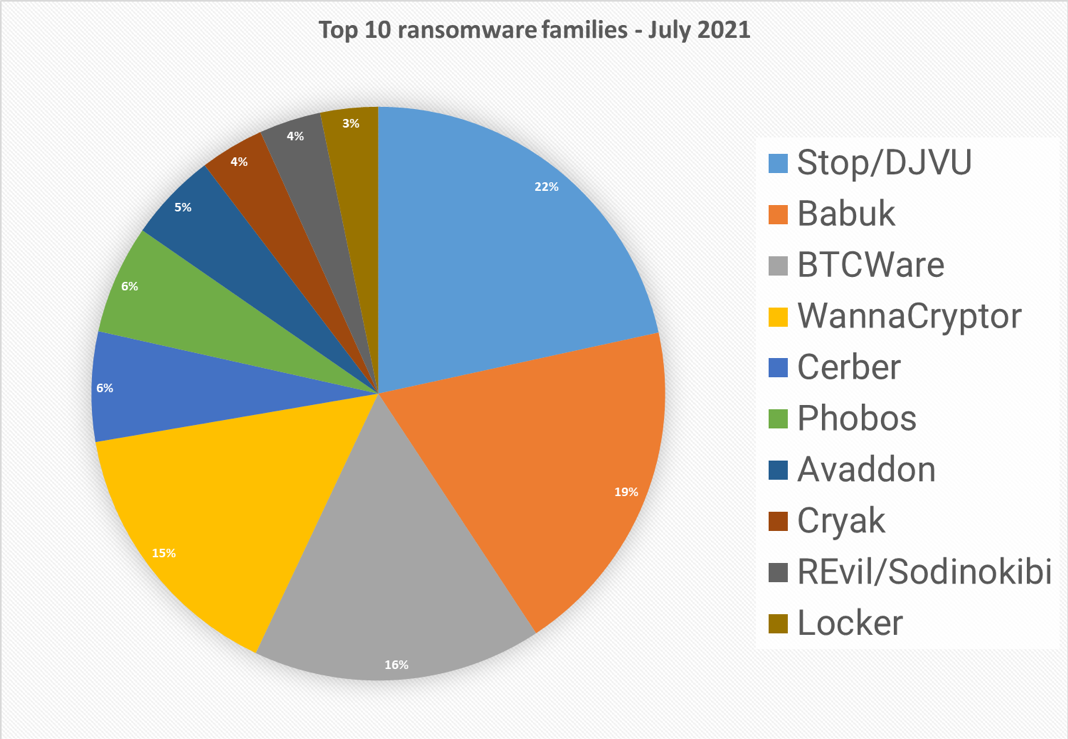
Top 10 ransomware families
Analyzing 21 million malware detections from July 1st to July 31st, 54,343 were identified as ransomware. Specific ransomware families are assigned to about half of them. In total, we identified 372 ransomware families.
Biggest Ransomware Offender
Stop/DJVU is the leading threat offender for the month of July and 2021 as a whole. This ransomware family primarily targets home users and is opportunistic (instead of large-scale targeted attacks like REvil or DarkSide). Stop/DJVU’s tactics are considered “classic” ransomware. By using algorithms to encrypt victim’s data on a computer or whole server, Stop/DJVU makes compromised files impossible to open or use. First detected in 2018, Stop/DJVU shows no signs of slowing down. One of the reasons we see Stop/DJVU so prominently is because our sample base includes telemetry from Bitdefender’s millions of consumer endpoints and telecom partners. While major attacks on businesses, healthcare and governments make the news, consumers are still a massive ransomware target.
Top infection Method: Compromised software is the most common infection method for Stop/DJVU ransomware. These are typically downloaded from cracked software, key generators, torrents, email attachments and other peer-to-peer networks.
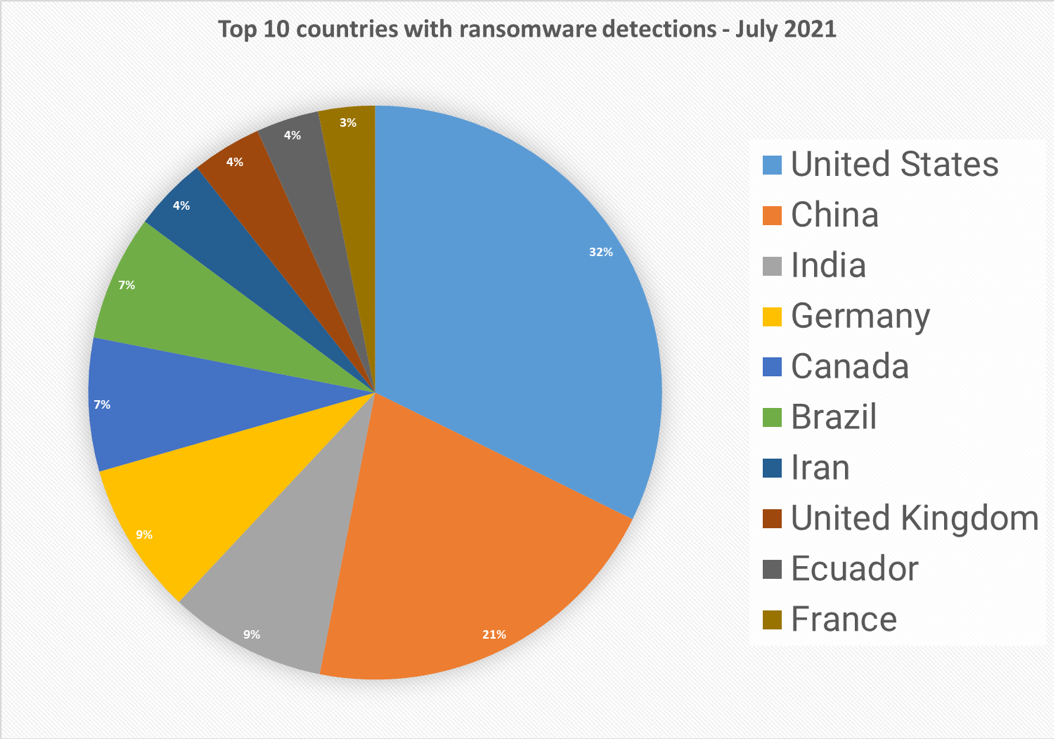
Top 10 countries
In total, we detected ransomware from 171 countries in our dataset this month. Ransomware is a global threat that has touched almost the entire world. Following is a list of the top 10 countries with the most ransomware detections. Overall, there are no big surprises here – since most of ransomware attacks are opportunistic, the size of population is correlated to the number of detections and large countries are leading our list.
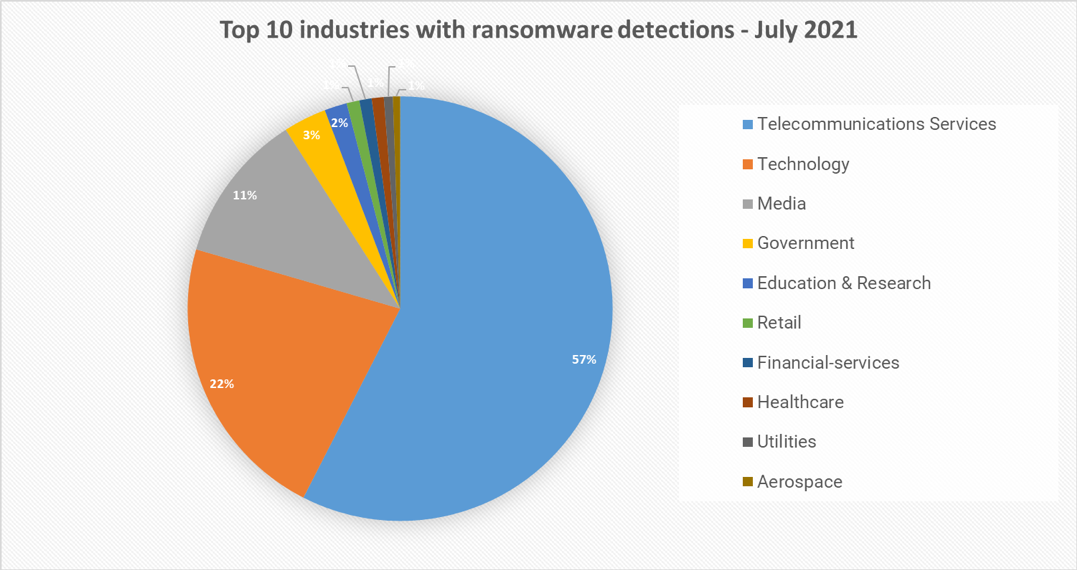
Top 10 industries
For our dataset, we have been able to assign almost 40% of detections to specific industries. Telecommunications and technology companies lead our findings at nearly 80% of overall detections. Telecommunications services is particularly high, because their customers are included in the detections. These findings also coincide with recent attacks against supply chain and service providers.
Summary
While major attacks on businesses make the news, consumers are a massive target. The ransomware landscape is diversifying. Some threat actors specialize in high-profile attacks that are planned for months; other groups are more opportunistic and focus on volume rather than the value of victims. To stay ahead of attackers, it is important to recognize the risks and the different tactics cybercriminals use to breach a system.
We hope you have found our first BDTD report interesting. Leave us a comment and let us know what you think. Don’t miss the upcoming BDTD for August 2021, subscribe to Business Insights blog or follow us on social media.
We would like to thank Mihai Leonte, Catalin Marculet, Dragos Teodor Gavrilut, Cristina Vatamanu and Vlad Craciun for their help with putting this report together.