
Some malware and phishing campaigns have short lives, tending to dissipate after they’re identified by security solutions. Others seem to survive year after year, with victims falling for the same tricks. Banking trojans such as TeaBot and FluBot and the “Is it you in the video?” scams are just two examples of threats that adapt to remain relevant.
The impact of TeaBot and FluBot trojans became apparent last year globally. Threat actors used mockups of popular apps, applications posing as ad-blockers and sent SMS messages from already-compromised devices to spread the malware organically. The banking trojans’ functionality are straightforward – they steal banking, contact, SMS and other types of private data from infected devices. They have an arsenal of other commands available, including sending an SMS with content provided by the command and control (CnC). This allows its operators to change targeted banks and other features on the fly, depending on the countries affected.
These threats survive because they come in waves with different messages and in different time zones. While the malware itself remains pretty static, the message used to carry it, the domains that host the droppers, and everything else is constantly changing.
Since the beginning of December, Bitdefender Labs intercepted over 100,000 malicious SMS messages tying to distribute FluBot malware by analyzing telemetry from the new Scam Alert feature, now available by default in Bitdefender Mobile Security & Antivirus. Findings indicate attackers are modifying their subject lines and using older yet proven scams to entice users to click. Additionally, attackers are rapidly changing the countries they are targeting in this campaign.
The following is a detailed overview of the findings:
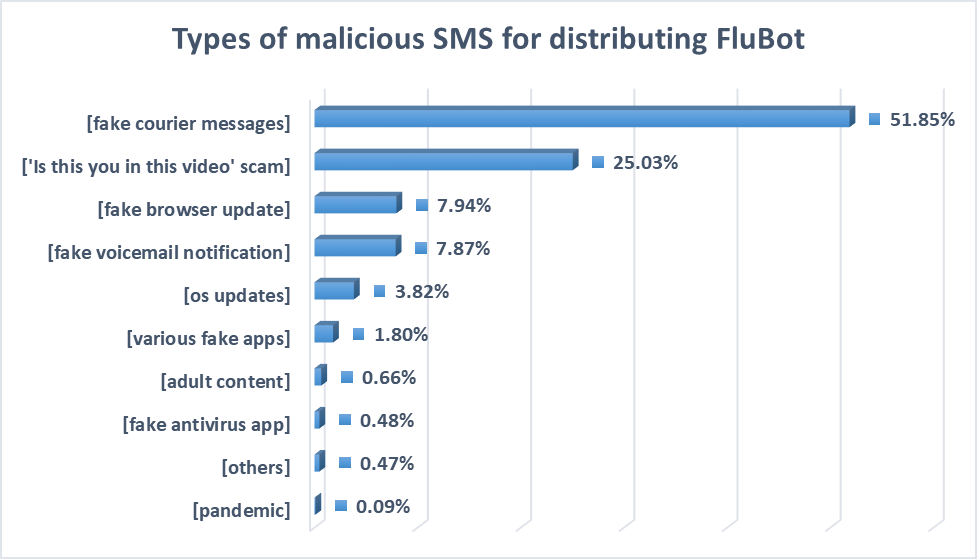
With the help of Scam Alert, we’ve seen how this malicious SMS now informs users of potential problems with parcel delivery and tells users that Flash player needs an update, that they have a missed voice mail or that some Android component needs upgrading.
FluBot distribution worldwide
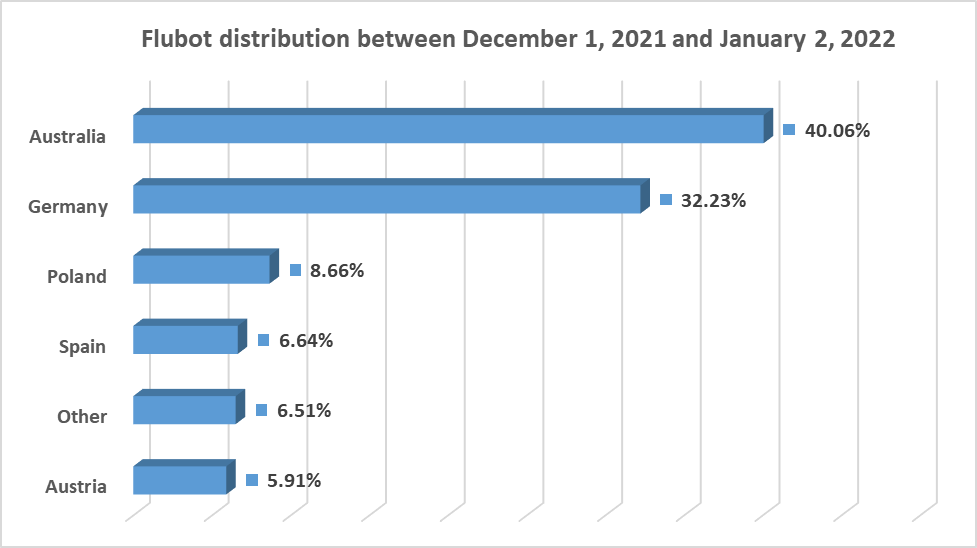
The FluBot operators target different zones for short periods – sometimes just a few days. For example, in the month between Dec. 1 of last year and Jan. 2 of this year, the malware was highly active in Australia, Germany, Spain, Italy and a few other European countries.
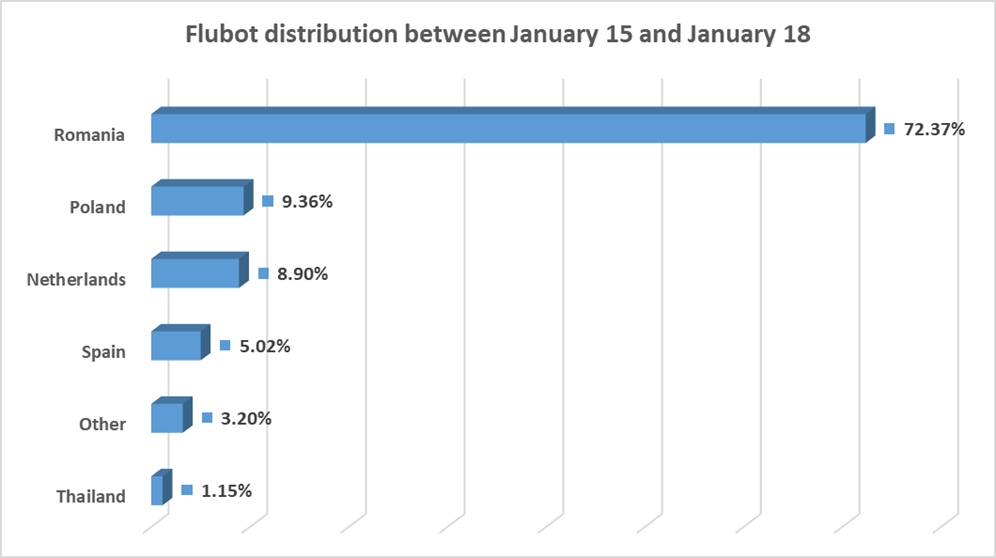
Starting Jan. 3, 2022 the attackers began to look at other countries to spread their malware, including Poland, Romania and the Netherlands. In fact, Romania has been one of the main targets in the past few days.
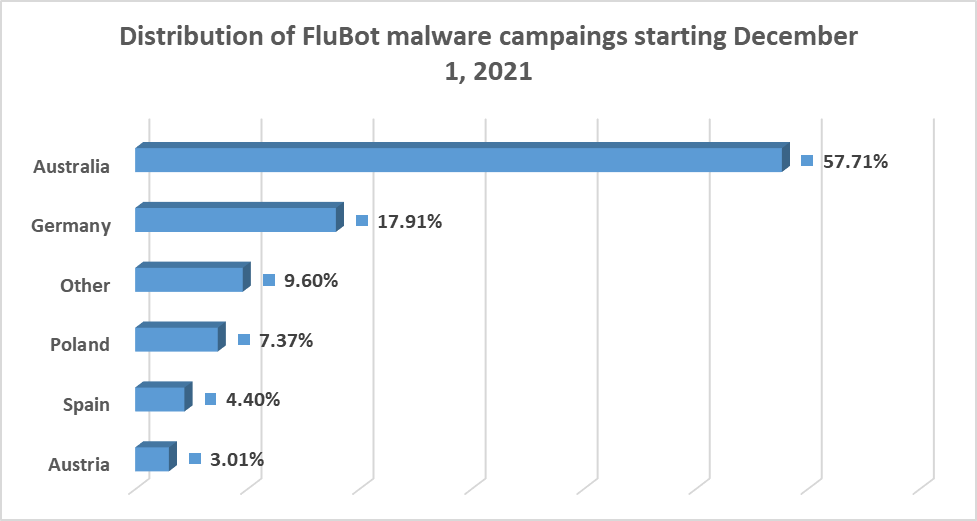
The worldwide distribution of the past couple of waves we’ve observed in the past couple of months shows Australia as a primary target.
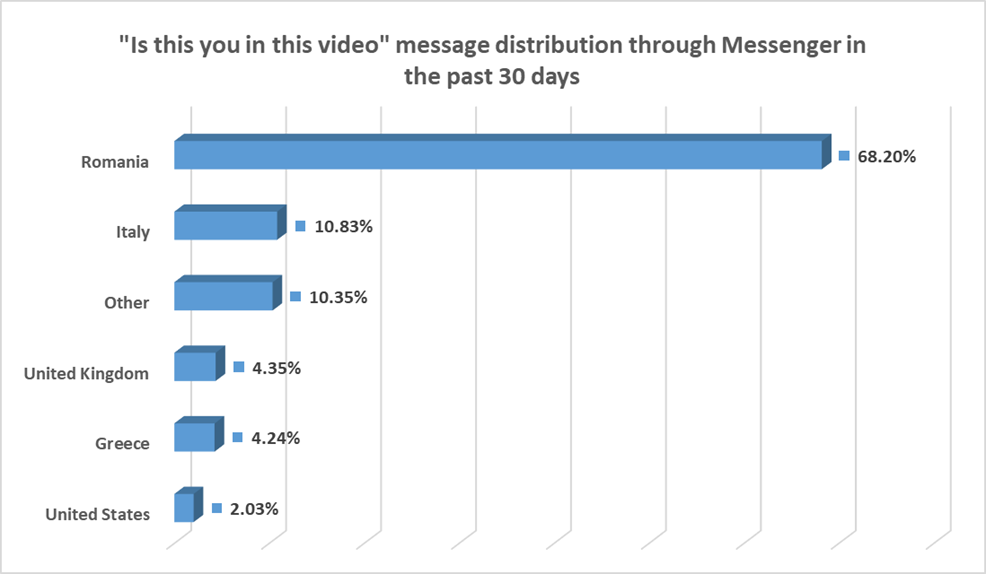
‘Is this you in this video?’ message adapted in FluBot campaign
A simple phishing campaign is still making the rounds on social media, primarily through Facebook’s Messenger. Users receive a message from a friend in their list with a question (“Is this you in this video?“ or some variation) and a link. When the victim clicks on the link, it usually redirects them to a fake Facebook login that gives attackers direct access to credentials.
The phishing campaign is already a couple of years old, and it’s persistent. It shows up on Facebook in waves and doesn’t seem to disappear. We mention this campaign because FluBot operators have adopted a similar message for their malware. In this situation, victims receive an SMS message along the lines of “Is this you in this video?.”
The goal is the same – to somehow mislead people into installing the software under some pretext, by telling them that Flash or some Android component actually needs an upgrade after they’ve opened the link informing them they could be in a video. This new vector for banking trojans shows that attackers are looking to expand past the regular malicious SMS messages.
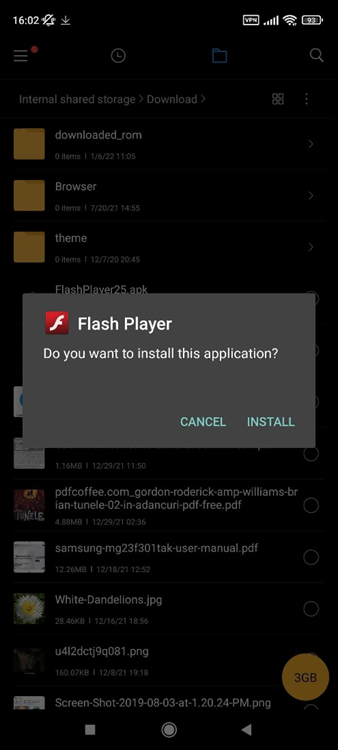
In fact, Romania has been one of the main targets in the latest “Is this you in this video?” campaign distributed through Messenger. We’ve intercepted over 10,000 malicious URLs just in the past 30 days. While the two campaigns are likely not related, it’s interesting to see how one group uses the methods of another.
New TeaBot campaign targeting official apps stores
Most believe the official Google Play Store is completely safe to download and vetted for security purposes before they become available to the public. That’s true most of the time but not always.
Sometimes malicious apps are missed and stay active on official stores accruing thousands of downloads before they are noticed and taken down. We found something strange during our investigation of the new FluBot campaign. We initially believed Flubot was being installed on devices without a malicious SMS being sent but discovered that a different malicious banking bot was installed on the same device.
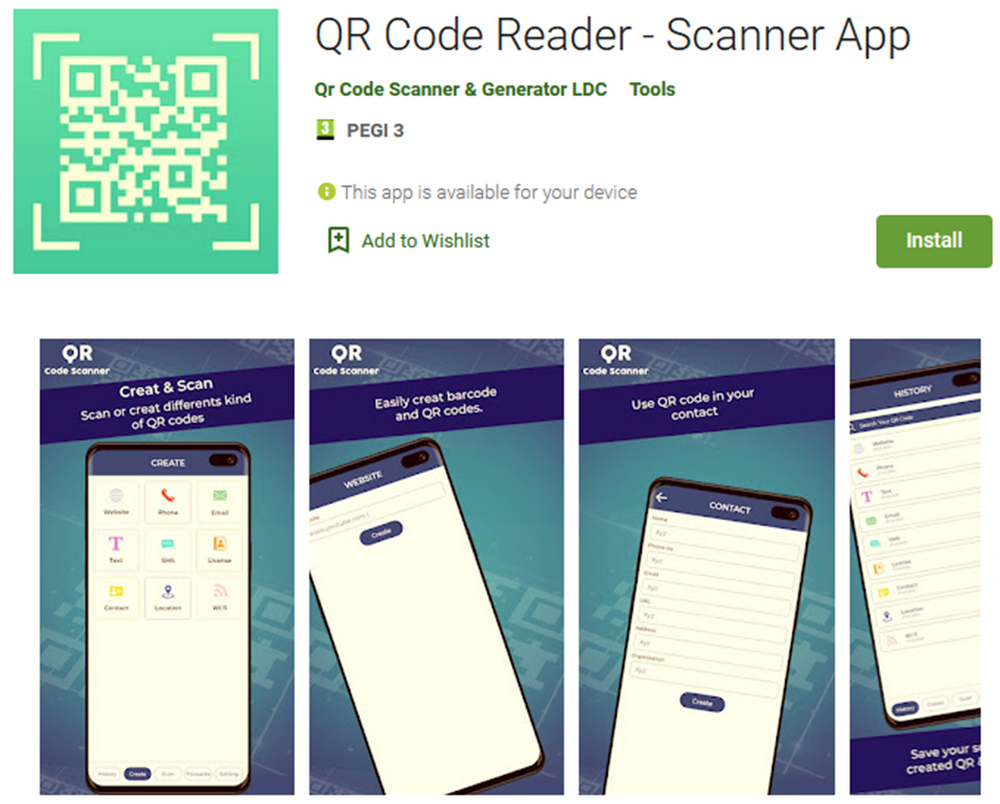
We determined it was a TeaBot variant, and further investigation led to the finding of a dropper application in Google Play Store named the ‘QR Code Reader – Scanner App’, with over 100,000 downloads, that has been distributed 17 different TeaBot variants for a little over a month.
Bitdefender’s security researchers have found that the ‘QR Code Reader – Scanner App’ found in the Google Play Store is likely a heavily encrypted TeaBot dropper. In just 30 days, it dropped 17 variants of the malware.
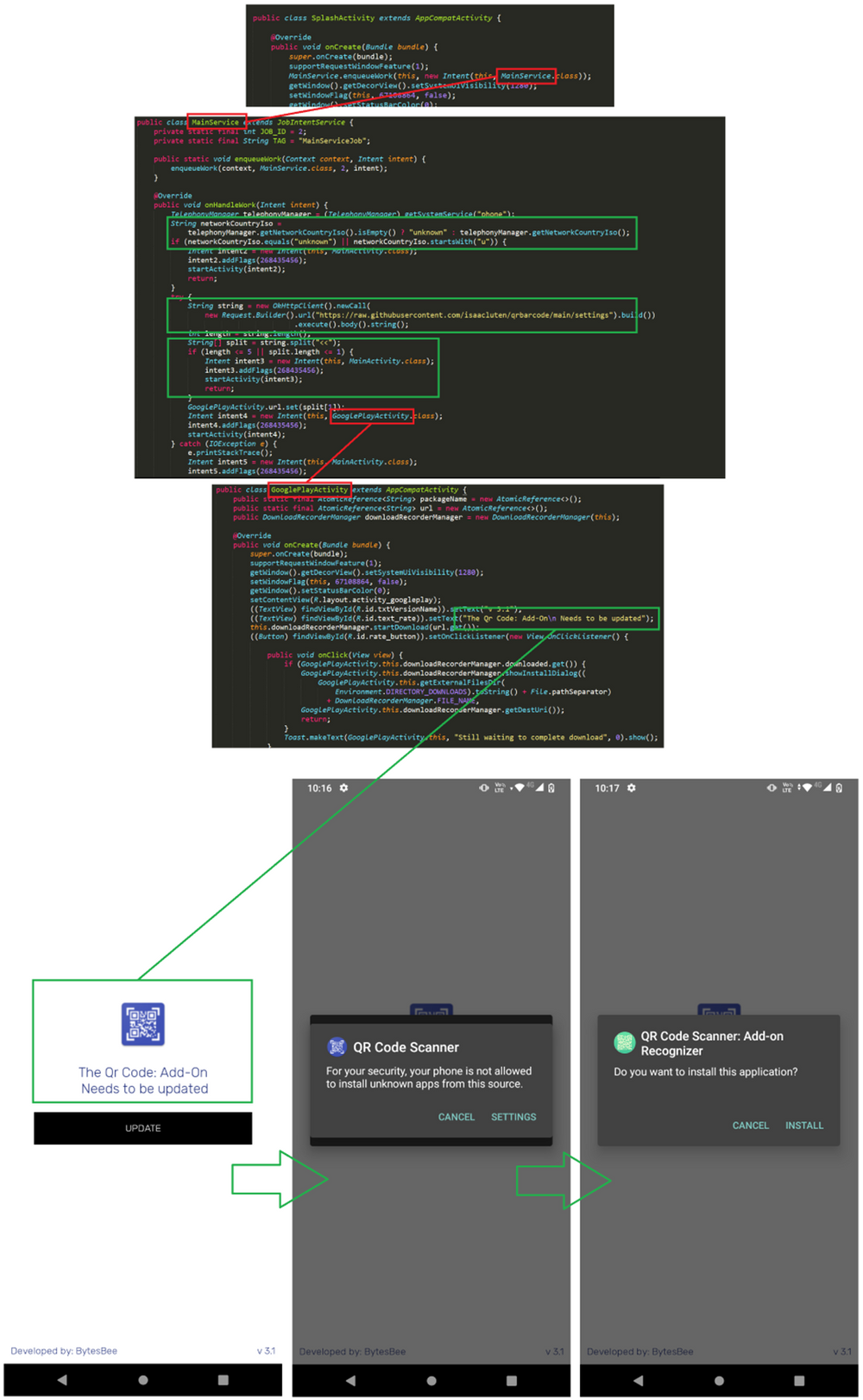
The application itself is not malicious, and it does offer the promised functionality, but that’s a known tactic. The malicious code within the app has a minimal footprint, as the authors were careful about not triggering security heuristics. The path followed after installation is relevant in itself.
When the user starts the Android app, it also starts a background service that checks the country code of the current registered operator (or the cell nearby). If the country starts with a “U” or is unavailable, the app skips executing the malicious code, which means that countries like Ukraine, Uzbekistan, Uruguay and the US are skipped.
If the app passes the check, it retrieves the context of a settings file from GitHub from the following address:
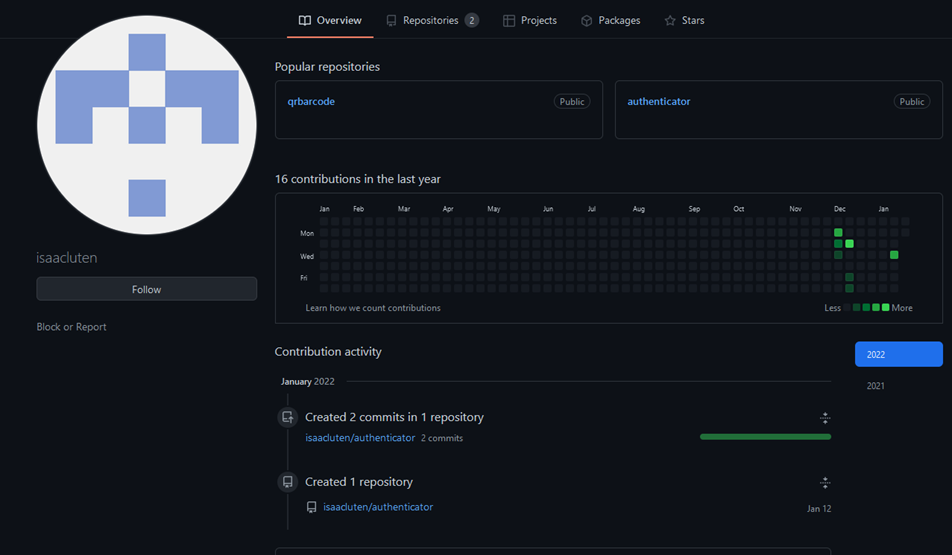
raw.githubusercontent[.]com/isaacluten/qrbarcode/main/settings
This file contains a different GitHub repository file link pointing to the actual payload to download.

This settings file, from the QR Code Reader repository, has the URL changed whenever a different payload URL is needed or even removed if the authors wish to deactivate the malicious behavior temporarily.
If there is a URL in the settings file, the APK is downloaded and saved to ‘/sdcard/Android/data/com.lorankey.qrcode/files/Download/addonqrapp.apk’, and the installation is initiated.
The app itself presents a fake UI saying that an update is required, and users are instructed to allow the Android app to install third-party packages.
Combining our telemetry with GitHub’s repositories history, we identified a minimum of 17 different versions of TeaBot that were deployed to victims from Dec. 6 of last year to Jan. 17 of this year.
GitHub accounts
The malware has a hardcoded GitHub URL to get the next payload (another GitHub URL). Looking at GitHub’s history and our own analysis, we have the following accounts associated with this threat:
|
GitHub user |
Timeline |
Purpose |
|
github.com/isaacluten |
Created 2021.12.06 |
Configuration files storage; indicates |
|
github.com/lotterevich |
First seen 2021.12.06 Last seen 2021.12.17 |
Held payloads, but was deleted |
|
github.com/rosamundstone393 |
Created 2021.12.07 |
FluBot payloads are currently uploaded |
Between the accounts, all payloads’ configurations seen were as follows:
|
Content of |
|
1.0.0<<https://github.com/rosamundstone393/maina/blob/main/today.apk?raw=true |
|
1.0.0<<https://github.com/lotterevich/lott/blob/main/today.apk?raw=true |
|
1.0.0<<https://github.com/lotterevich/lott/blob/main/fullymain.apk?raw=true |
|
1.0.2 |
|
1.0.1 |
|
1.0.0<<https://github.com/lotterevich/lott/raw/main/maina.apk |
|
1.0.0 |
|
1.0.0<<https://github.com/lotterevich/lott/raw/main/Flashlight.apk |
Currently, all payloads are uploaded as “1.0.0<<hxxps://github.com/rosamundstone393/maina/blob/main/today.apk?raw=true”
There is one repository for payload configuration for the QR Code Reader app, and another repository was created for an app named 2FA Authenticator, also a dropper, that was just released.
Telemetry
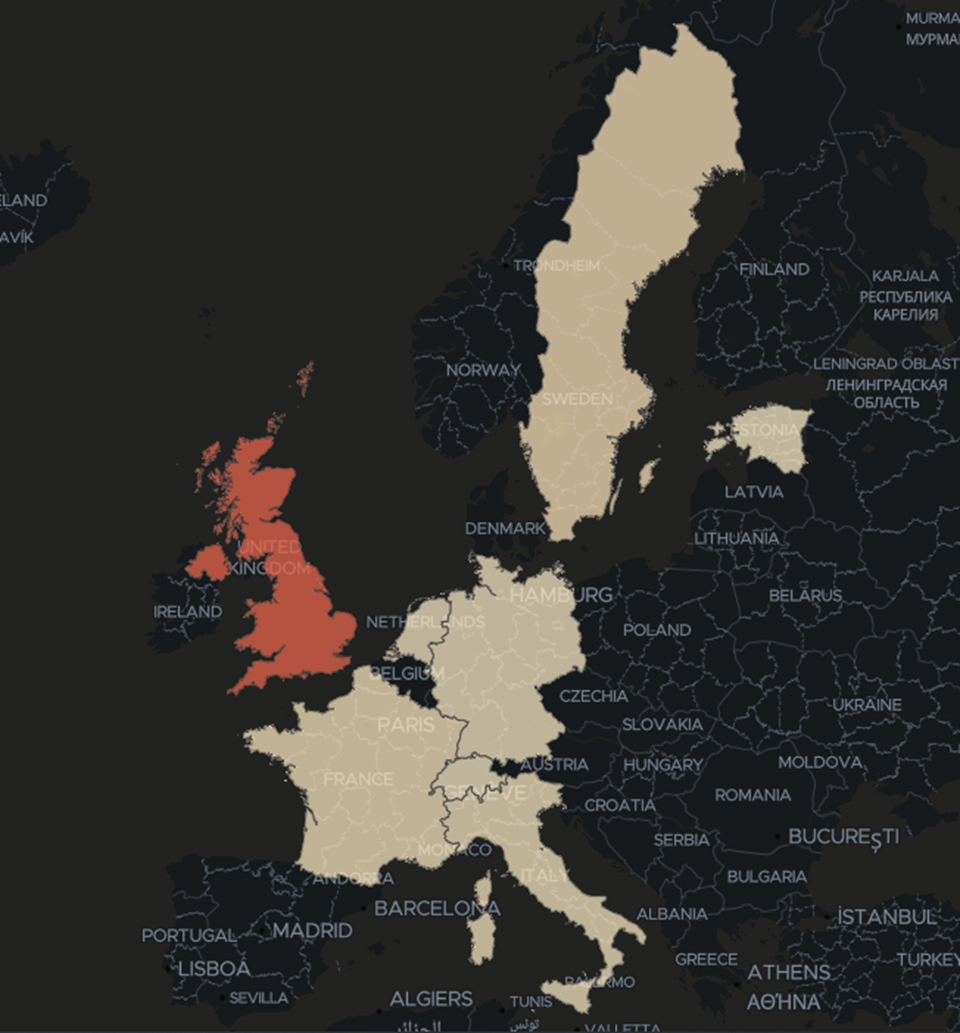
The QR Code Reader application is available for download globally but, oddly, our telemetry shows the vast majority of scans on the dropped payloads come from Great Britain. We presume that the authors of the malware have made specific ad campaigns targeting that area.
Bitdefender’s security researchers also found one of the ways this app manages to spread through the userbase. Victims likely see an ad for this malicious app in other legitimate Android applications and install it through that vector. The attackers pay to appear in Google Ads, giving them screen time in an app that could have millions of users.
The 2FA Authenticator we found is a similar malicious dropper currently available on the Play Store. Fortunately, this version of the malware dropper had no chance to infect as many victims because we caught it as soon as it was released.
All countries that are excluded by the malware by ISO codes:
|
‘UG’ |
‘UGANDA’ |
|
‘UA’ |
‘UKRAINE’ |
|
‘US’ |
‘UNITED |
|
‘UM/UMI’ |
‘UNITED |
|
‘UY’ |
‘URUGUAY’ |
|
‘UZ’ |
‘UZBEKISTAN’ |
Google Play Store maybe not as safe as you think
Searching for similar dropper behavior, we found other applications that used to be available on Google Play and distributed TeaBot. As far as we can tell, they’ve been silently removed without anyone noticing they were ever live.
|
App name |
App package name |
Developer |
Last known download count |
Last seen on Play |
|
QR Scanner APK |
com.paccinisantino861.qrscanner |
santino paccini |
10,000+ |
2022.01.07 |
|
QR Code Scan |
com.scannet.qrbar |
Bailey Leightonware |
10,000+ |
2021.04.21 |
|
Smart Cleaner |
com.butkusnedas.smart.cleaner |
Butkusnedas |
1,000+ |
2021.12.17 |
One relevant feature for this malware is the complete lack of malicious code in the initial versions. Attackers initially submit clean apps and introduce the malicious component in subsequent updates. The three apps mentioned above provide the perfect example of this behavior.
|
App name |
Version code |
Version name |
APK MD5 |
|
QR Scanner APK |
4 |
2.4 |
bea21055cda8c81b4e5a46c1fac2b570 0f621dbe75d1d223353e9a74209c43cb |
|
QR Code Scan |
4 |
1.03 |
125a0b5013e3ef4b6a4af2d184b68a0b |
|
Smart Cleaner |
2 |
2.0 |
77dd1738f3109a15a9b38db2845bbb54 |
|
3 |
3.0 |
1c486fe75688a2fd67b26c22d0f85adc df7770114becbbee2f06be8947039c31 |
Rough weather we’re having
The Weather Cast application by Weather Live is an active app on Google Play that also drops banking malware. Determining the exact nature of the malware is challenging because threat groups copy much of the code from one malware to another, following up with heavy encryption to obfuscate the code. In the end, this only makes it more difficult to pinpoint the exact version. It doesn’t affect the ability of Bitdefender’s Mobile Security & Antivirus to stop the malicious behavior.
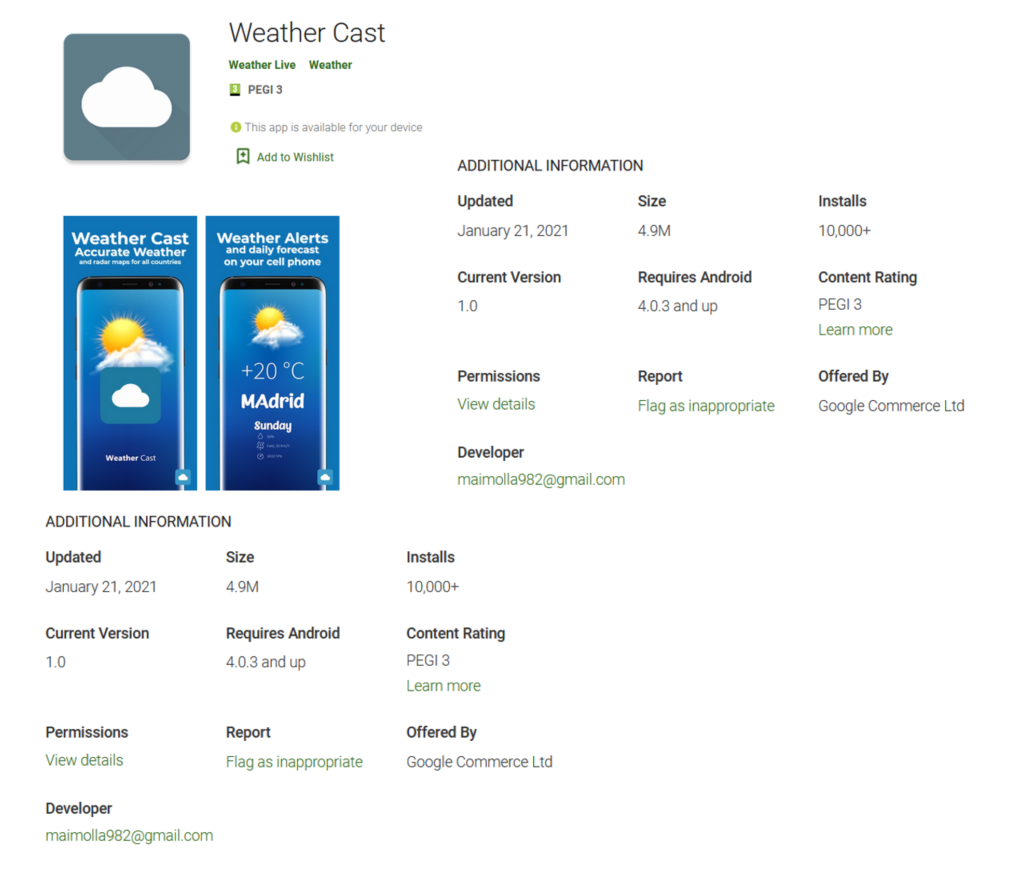
This malicious dropper retrieves the malware from its firebase (weather-live-a2756.firebaseio.com) database:
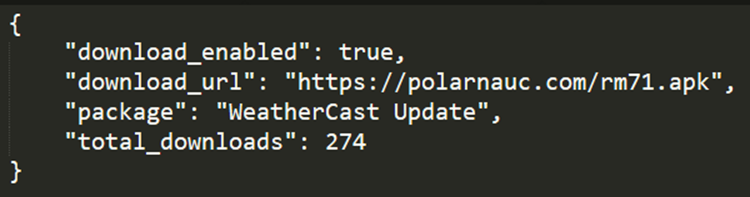
The firebase currently indicates that this banking malware has been dropped on 274 victims, but the actual number could be a lot bigger, given that the app is not new. It’s also likely that 10,000 downloads indicated on Google Play are not all real user downloads.
The malicious payload is saved as SampleDownloadApp.apk on the file system and triggers the regular to install.
Currently, although the firebase returns the download URL is currently down (polarnauc.com/rm71.apk), our telemetry indicates that victims downloaded the malicious banker trojan app.
|
Weather Cast dropper application |
|
05a041e47e305a4b2327f0e46d9d385f 7392e69e36ceb88425c1d8a421976a0d 773f698e035cfe0a9b642428a028405f d600c4a4466da09e239c855e19addd5a 575c0d28e7bf5198ffe7bf5950e119f4 e652412ac7de94fdfcb7c2a6e4a0fcc0 |
Another weather application we found is named Weather Daily from WeatherDaily, and it’s still on Google Play, with the same malicious download capability.
This application has the same firebase URL used in our first, thus it is also inactive at this point.
|
Weather Daily dropper application |
|
906166b5f0478083002fa2766f7f1cce bbefb28d7bdf997ac4d5ad747f62a0b3 9eb12035c0539b768e25581c9a425ff6 12dc7c3768430ade2ff4d2533bad5fb5 01b347ab6b147c02b20cef61bc50089b 568fbec1a9696da35af3c7dc277d6397 8cb1700b8bc2b92ef767bc04f4f02189 5a5ecf6b28bcae06b590df3a622c4401 7da32784fa162e59b216d7ea21476520 cdba81c1e0e9be347dd3072b2bcfb335 8dff2bd7449f510bed9c0949432dda9f 424c34c7d4ab5b9a808d2df211551336 48e3c1b0bf0c8efcf78e26605c74fa3c 7fe5ffbd394e5a92b649fa44a6cca1d3 3625dcca6b829d888235e001eff9f069 |
Indicators of compromise (IOC)
We already notified Google and GitHub regarding all of this malicious activity and GitHub took down the accounts.
|
Dropper MD5 |
Dropper package name |
|
6be155472cedc94d834a220b6217c029 |
com.lorankey.qrcode |
|
125a0b5013e3ef4b6a4af2d184b68a0b |
com.scannet.qrbar |
|
57f6576705e7e8b11fbd3480b7602f25 |
com.qrcodeapp.qrcodeapp |
|
77dd1738f3109a15a9b38db2845bbb54 |
com.butkusnedas.smart.cleaner |
|
1c486fe75688a2fd67b26c22d0f85adc |
com.butkusnedas.smart.cleaner |
|
df7770114becbbee2f06be8947039c31 |
com.butkusnedas.smart.cleaner |
|
bea21055cda8c81b4e5a46c1fac2b570 |
com.paccinisantino861.qrscanner |
|
0f621dbe75d1d223353e9a74209c43cb |
com.paccinisantino861.qrscanner |
|
05a041e47e305a4b2327f0e46d9d385f |
com.weatherlive.android |
|
7392e69e36ceb88425c1d8a421976a0d |
com.weatherlive.android |
|
773f698e035cfe0a9b642428a028405f |
com.weatherlive.android |
|
d600c4a4466da09e239c855e19addd5a |
com.weatherlive.android |
|
575c0d28e7bf5198ffe7bf5950e119f4 |
com.weatherlive.android |
|
e652412ac7de94fdfcb7c2a6e4a0fcc0 |
com.weatherlive.android |
|
906166b5f0478083002fa2766f7f1cce bbefb28d7bdf997ac4d5ad747f62a0b3 9eb12035c0539b768e25581c9a425ff6 12dc7c3768430ade2ff4d2533bad5fb5 01b347ab6b147c02b20cef61bc50089b 568fbec1a9696da35af3c7dc277d6397 8cb1700b8bc2b92ef767bc04f4f02189 5a5ecf6b28bcae06b590df3a622c4401 7da32784fa162e59b216d7ea21476520 cdba81c1e0e9be347dd3072b2bcfb335 8dff2bd7449f510bed9c0949432dda9f 424c34c7d4ab5b9a808d2df211551336 48e3c1b0bf0c8efcf78e26605c74fa3c 7fe5ffbd394e5a92b649fa44a6cca1d3 3625dcca6b829d888235e001eff9f069 |
com.app.weatherclient |
|
3b24fc4b75c3a2a3016a1aadab12f4b7 |
org.otpauthverified.android.andotp |
|
TeaBot payload MD5 |
|
11d60ea8b765805fd21ccaa394c0f1c5 |
|
199a05563aac440df1ece5900dc8728b |
|
243063fdfc605e52e415286d441c64cd |
|
27c7610b496812ab44734d02ab84298e |
|
3acd1e3fc3a9748fee13550cfe86491f |
|
3ed22780949ae9c756186451b12e49c9 |
|
63889a8f68d33314435be05e519b2121 |
|
761d47788376087a8d9ebd79966d17ce |
|
8e9a27c2b2c78282536e747adbc32ff1 |
|
933e4941511c990c05c1a2f536eb73f2 |
|
c4648f55a3325853f435ce04b226eca5 |
|
d35101685436f5599d314e2843647424 |
|
db3ba9bd23563c720d793e397fc4db80 |
|
e5a3d989403bdc03132c1f5092a8d3fa |
|
f25da3ec09dbc26c30fd0734500f607b |
|
ff6184928f9704b482d4b7e157bf479c |
|
ffe5cb26952d97864dc643091450bd16 |
|
23e49cc28a5feeed4b9e362aa43e158a |
|
770b95a7894b32b139a9bf93bfaf7d26 |
|
ad96f5c40a8bdff8c682ecb7982aa19d |
|
0333d85a2c9e36ea7a84aad42b69e969 |
|
0801afc7101311e76e1b38484e19cec6 |
|
3cf74827168efbcd58633b929b4f6e94 |
|
5e81fc20f164ca96f3b57338493c4fcf |
|
Weather app |
|
cbd060ded5a83b5f874901e8c60bfb3d |
|
2776882a50b86a5829b7063fdcbe256f |
|
6ad5b3b9275df2cbf1671af2f7ae25e2 |
|
0585c9238714c5c44614e1594e73287e |
|
d3a1b6a21d4601cc6cd6a675790eda4b |
|
Weather app |
|
polarnauc.com/rm71.apk |
Associated GitHub accounts:
|
GitHub user |
|
github.com/isaacluten |
|
github.com/lotterevich |
|
github.com/rosamundstone393 |
This article is available courtesy to the Bitdefender Mobile Threats team.